This tutorial is also available as a video. Click on the video below or click this link.
In this article, you'll see how to create a catchy, good-looking Github profile page. By the end of the tutorial, your README will:
- update automatically with your latest blog articles/YouTube videos
- show your GitHub stats
- display the icons of your tech stack
Pre-requisites
Before going further, there are some pre-requisites for this tutorial:
- You should have a GitHub account
- You should be familiar with markdown
These are the only two pre-requisites for this tutorial.
1. Create a special README
The first step is to go to your GitHub page and then to the repositories tab. After that, click on the green button saying "New" so you create a new repository. Alternatively, use this link to create a new repository.
For the new repository, you need to use the same name as your GitHub username. For instance, my GitHub username is catalinpit, so the repository name is the same - catalinpit. In the figure below, you can see that you get a message automatically saying that it's a special repository.
When it comes to the description, add something that describes the repository. Also, make sure the repository is public and not private.
Lastly, click on the checkbox saying Add a README file to initialize your project with an empty README file. The reason is so you can create and customize the profile in the browser rather than downloading it on your machine.
After that, click on the green button saying "Create repository". In the figure below, you can see what I did to create my GitHub profile.
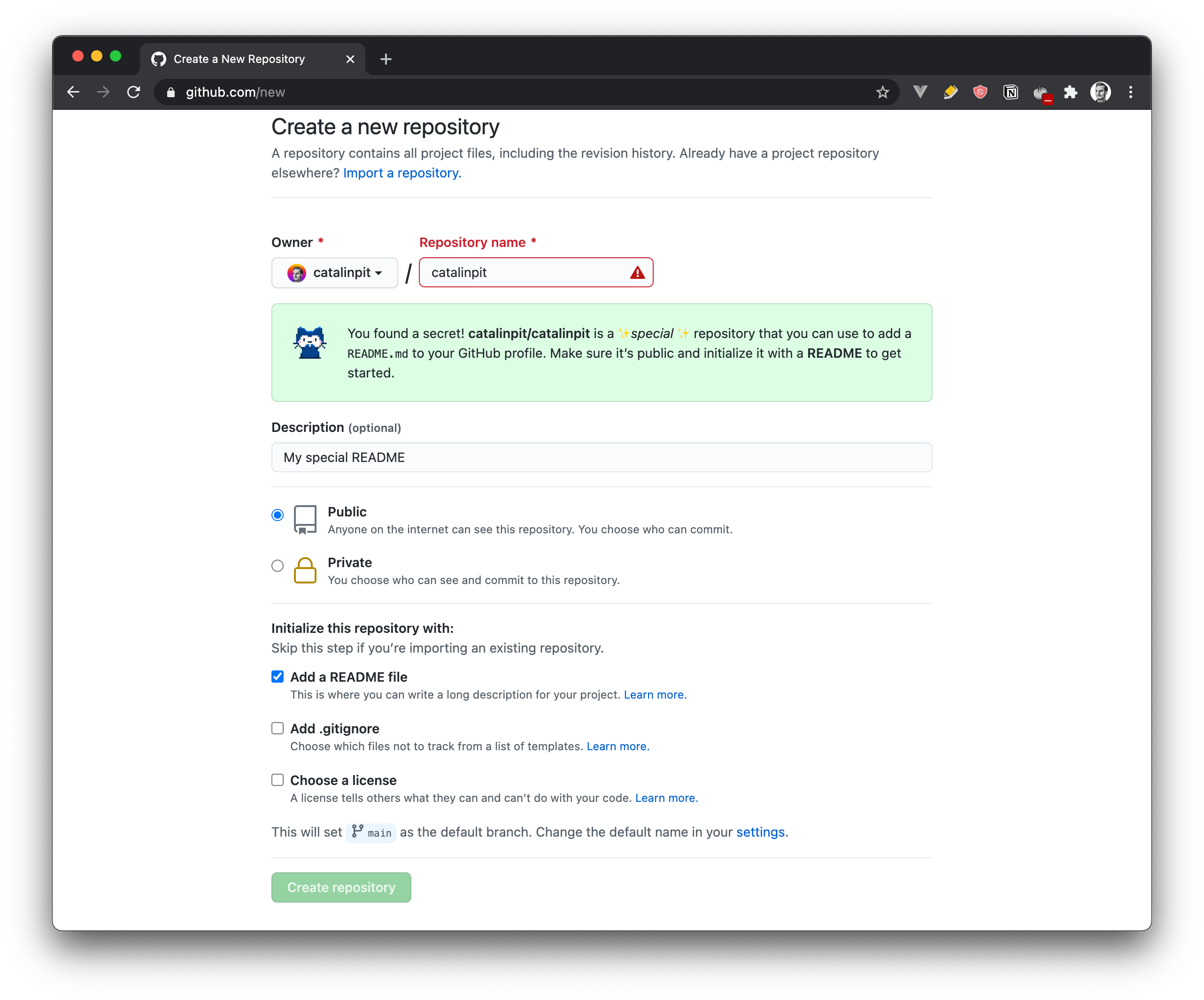
Note: In the image, you can see an error because I already have the repository, so I cannot create it twice. But if you do it for the first time, it will work properly!
2. Add the heading
Now that you have the special repository set up, you can start customizing it. The first step is to add a header to the profile. In my case, I use the following title:
### Hi there <img src="https://raw.githubusercontent.com/MartinHeinz/MartinHeinz/master/wave.gif" width="30px">, I am Catalin Pit!
The image is a hand that waves. The screenshot below illustrates how the above line looks in action.
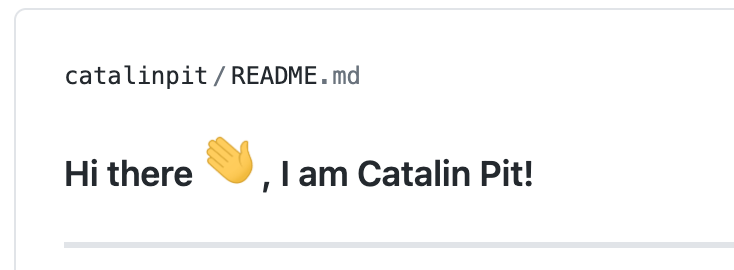
This is just an example, and that's what I use on my profile. However, you are not limited to it, and you can create a better headline.
3. Add social media badges
The next step is to add social media badges to your profile, like the ones in the figure below.
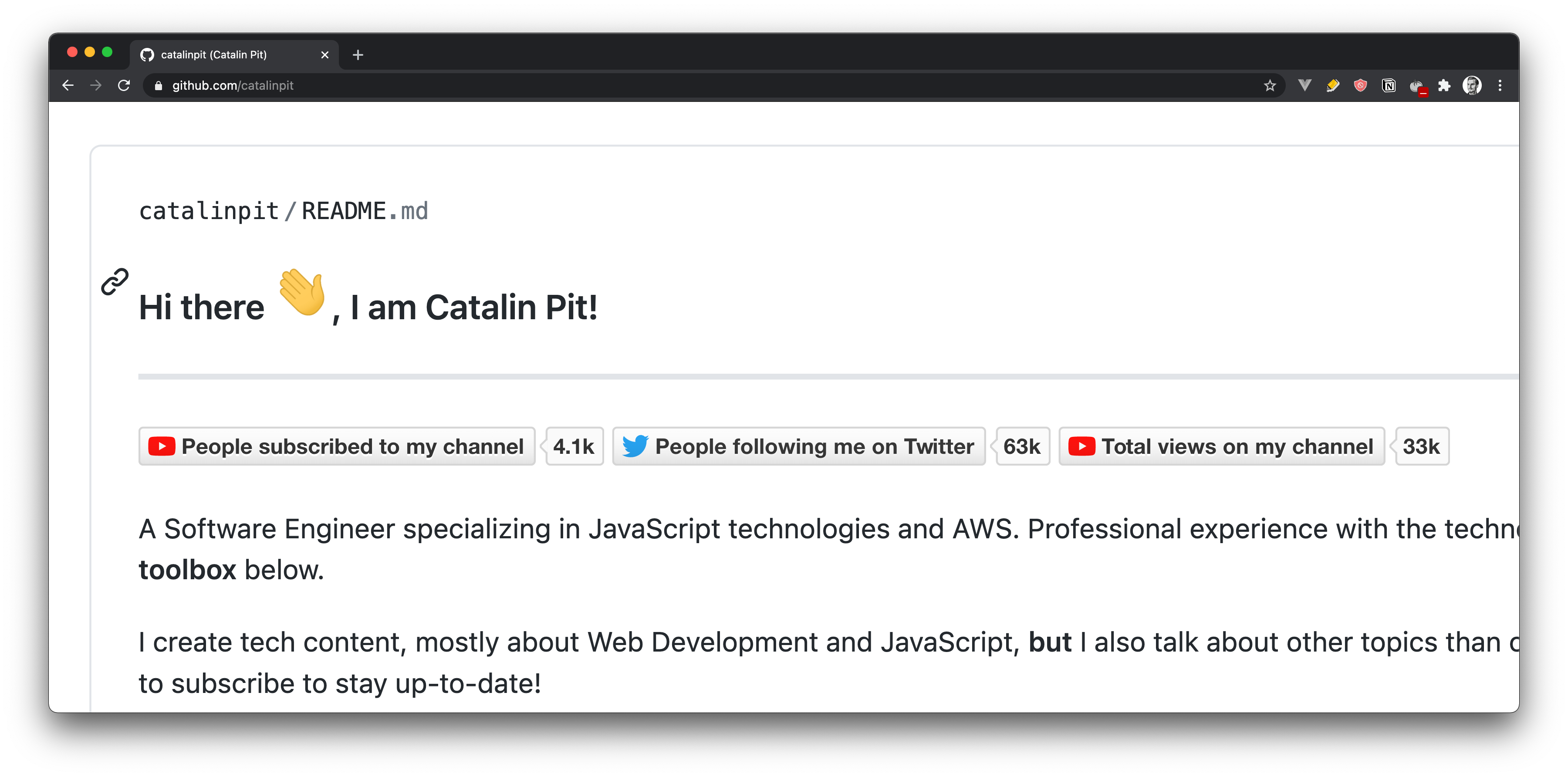
There is a particular site that generates these called shields.io. On this website, you can generate such informative badges for:
- GitHub
- YouTube
- Twitch
Let's say you want to add your Twitter follower count. Go to the shields.io website and click on the "Twitter follow" button, as shown in the image below.
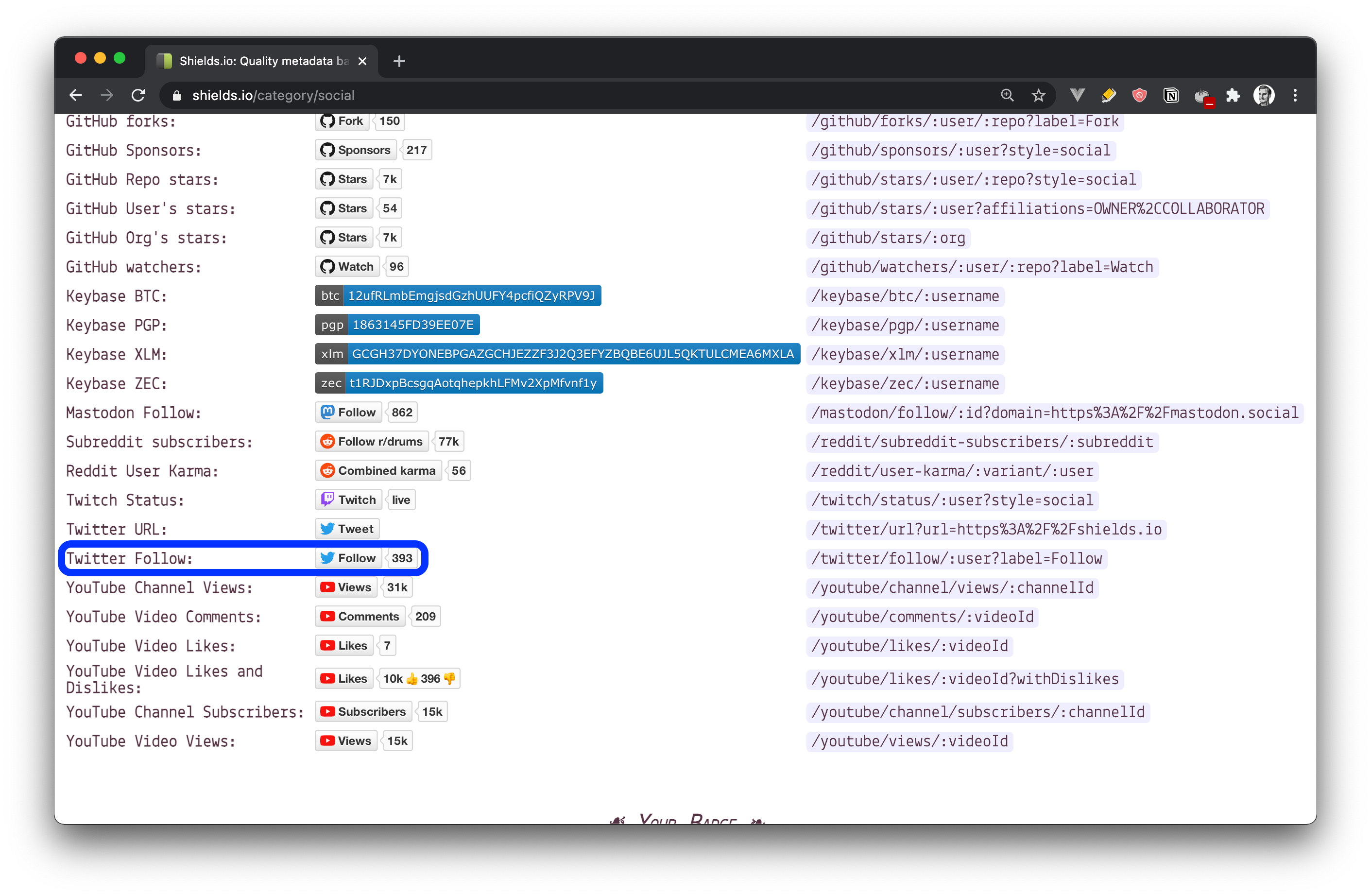
After you click on that button, you get a pop-up where you can customize the button and add your details. In the first field, you need to add your Twitter username.
However, you can leave the other fields blank. Their purpose is to allow you to customize the badge. For instance, you can replace the default text by entering a value in the field override label. Similarly, you can use other logos and colours by specifying them.
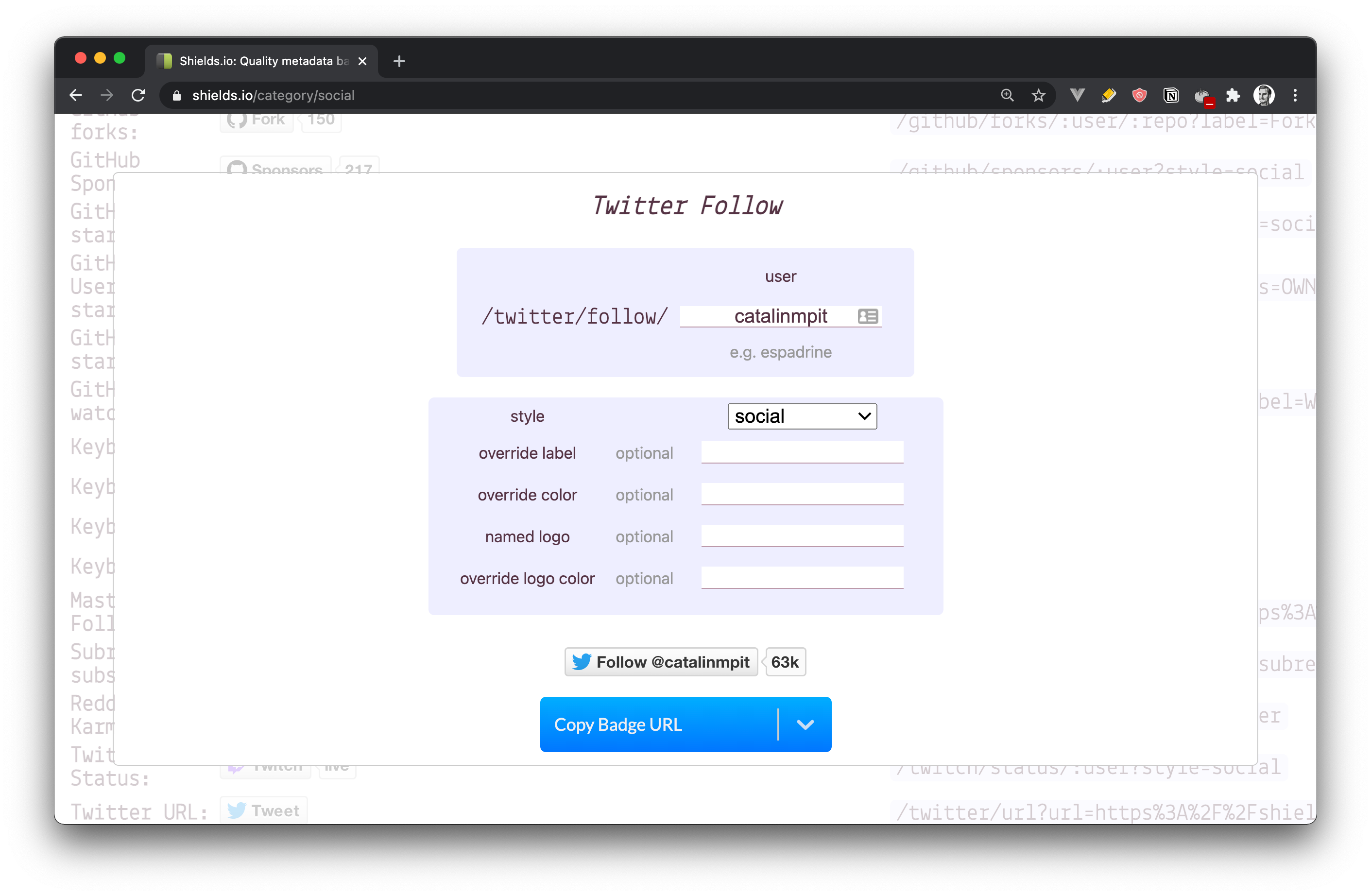
Once you are done with the badge, click on Copy Badge URL and then choose the option saying Copy Markdown. Once the badge code is copied to your clipboard, you can add it to your GitHub profile.
4. Add bio
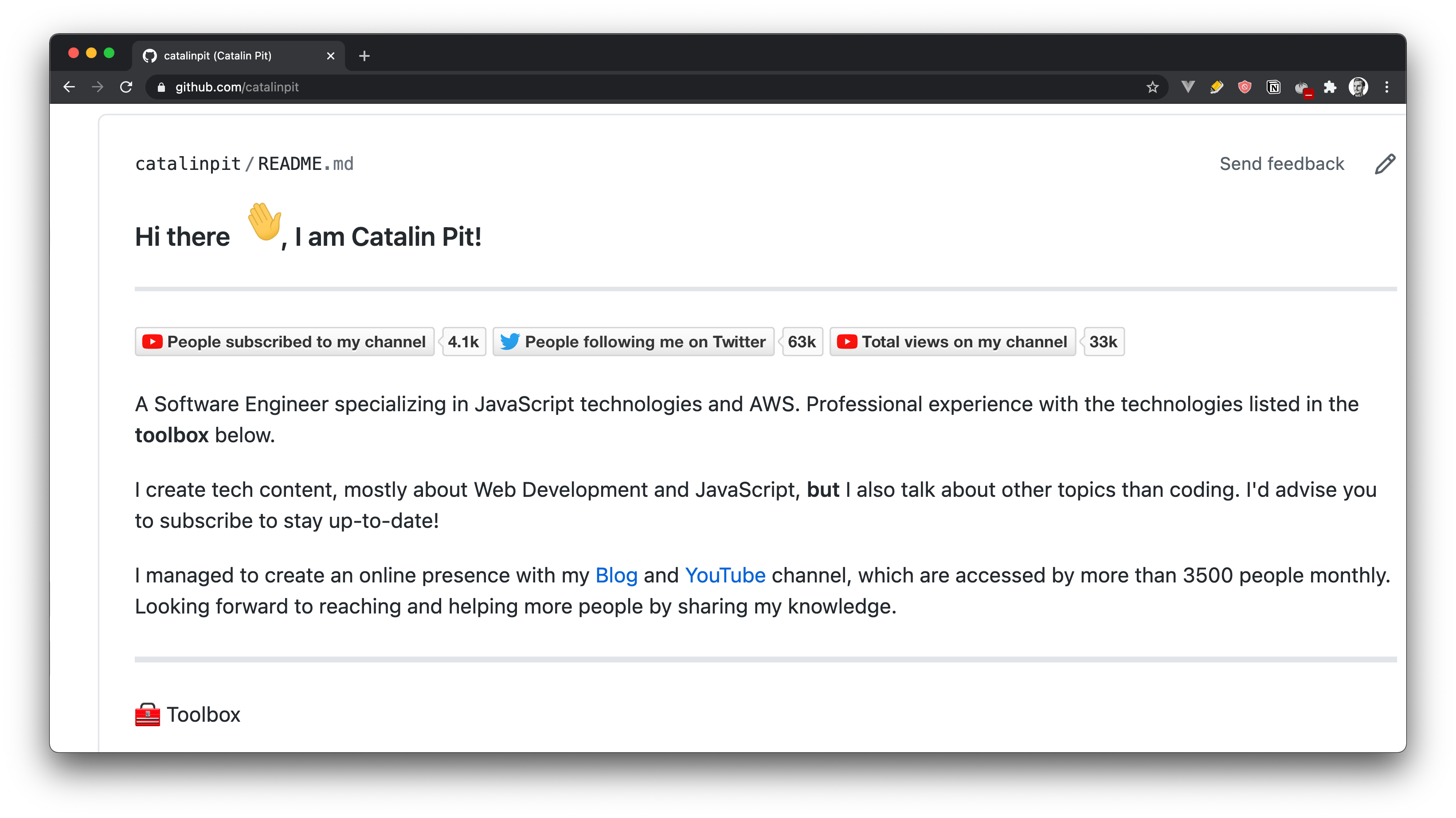
The fourth step is to add your bio. In this step, there is not much I can advise you. I embedded a screenshot of my GitHub profile so you can see an example.
However, you should add something unique, and that describes yourself the best.
Progress check
Before moving onto the following steps, let's make sure you managed to get up to this point. By this point, your GitHub profile should look something like this:
### Hi there <img src="https://raw.githubusercontent.com/MartinHeinz/MartinHeinz/master/wave.gif" width="30px">, I am <enter your name>!

<your_bio>
---
In the above markdown snippet:
- The first line is your heading
- The second line is the badge you generated on the
shields.iowebsite - The third line is your bio
- The three dashes
---are a section separator
5. Add the toolbox icons
The fifth step is about adding icons of your tech stack. The image below illustrates the technologies I use and their logos.

There are two websites you can use to find the logos of almost any technology. They are as follows:
- Devicons - "devicon" is a GitHub repository, and it aims to store all logos representing development languages and tools.
- WorldVectorLogo - The "WorldVectorLogo" website has SVG logos for almost any brand you can think of.
After your bio, add the following markdown snippet:
---
🧰 Toolbox
---
Now find the icons you need on the websites mentioned above. Once you have them, copy the SVG URL, and add it under the "Toolbox" heading.
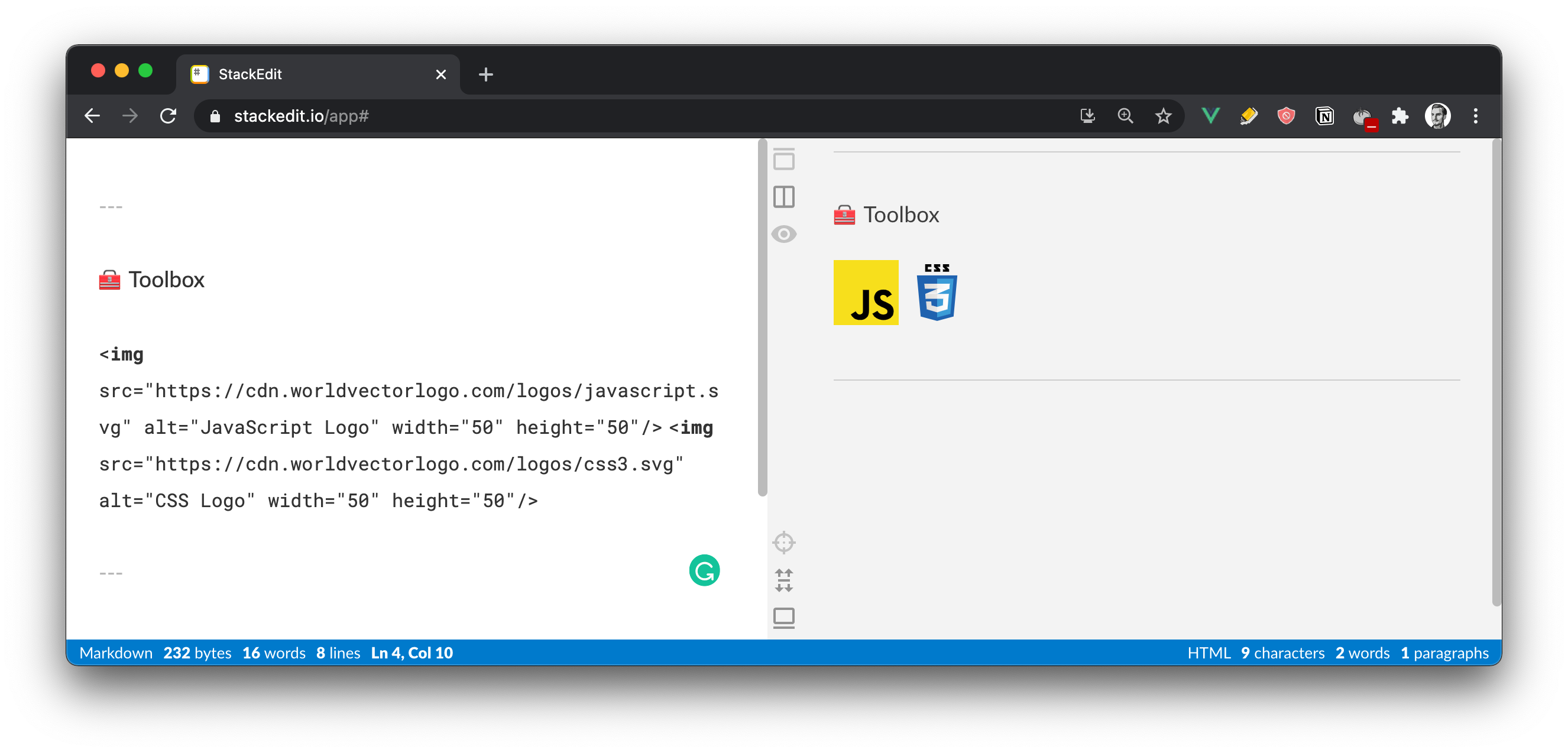
Let's say you found the JavaScript and CSS SVGs on the "WorldVectorLogo" website. You simply add the logo by using the img HTML tag, as shown in the snippet below.
---
🧰 Toolbox
<img src="https://cdn.worldvectorlogo.com/logos/javascript.svg" alt="JavaScript Logo" width="50" height="50"/> <img src="https://cdn.worldvectorlogo.com/logos/css3.svg" alt="CSS Logo" width="50" height="50"/>
---
The figure below illustrates how your Toolbox looks after adding the icons. From here, you can add as many you want or the ones that represent your tech stack. The purpose of this section was to get you started.
6. How to create GitHub actions
Before fetching the latest videos and blog articles, you need to set up two GitHub actions. Thus, in this section, you'll see how to do that.
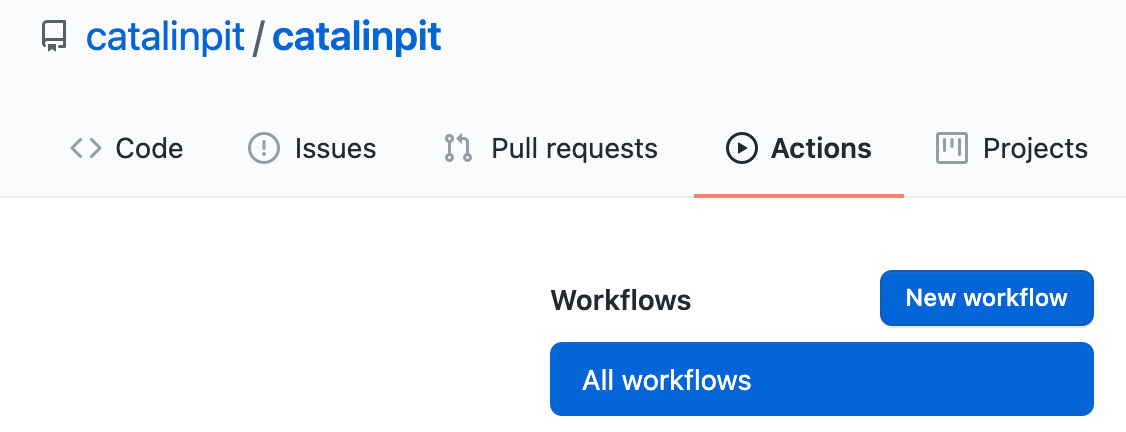
The first step is to go to your special repository (the one you created in step 1) and click on the Actions tab. After that, click on the button saying New workflow. The image below shows what you should see.
After you click on the button saying "new workflow", you are taken to the "Actions" page. There, you can see workflow templates you can use in your repository.
There is also a suggestion for your repository - "Workflows made for your repository". Choose the "Simple workflow" and click on the button saying Set up this workflow. The image below illustrates what you should see.
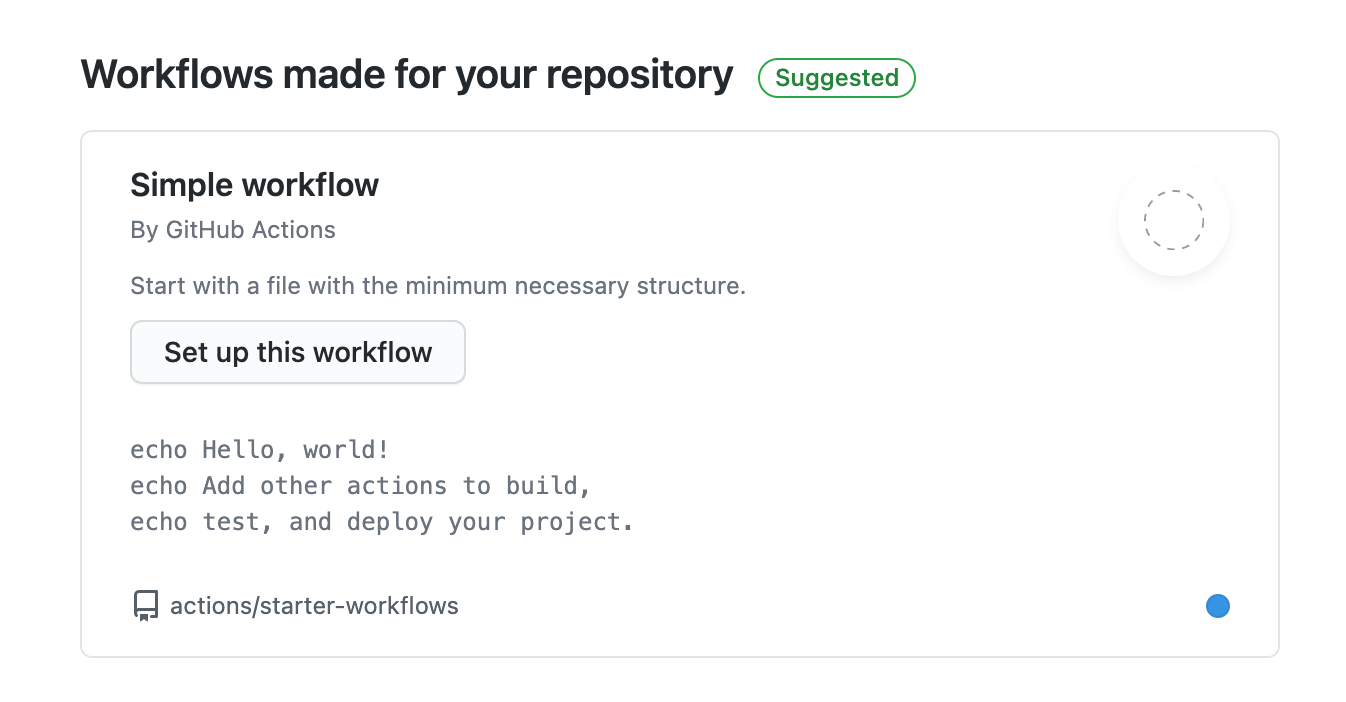
That's all you need to know to follow this tutorial. You'll use the same steps to create the necessary workflows to fetch both the articles and videos.
7. Fetch videos and articles
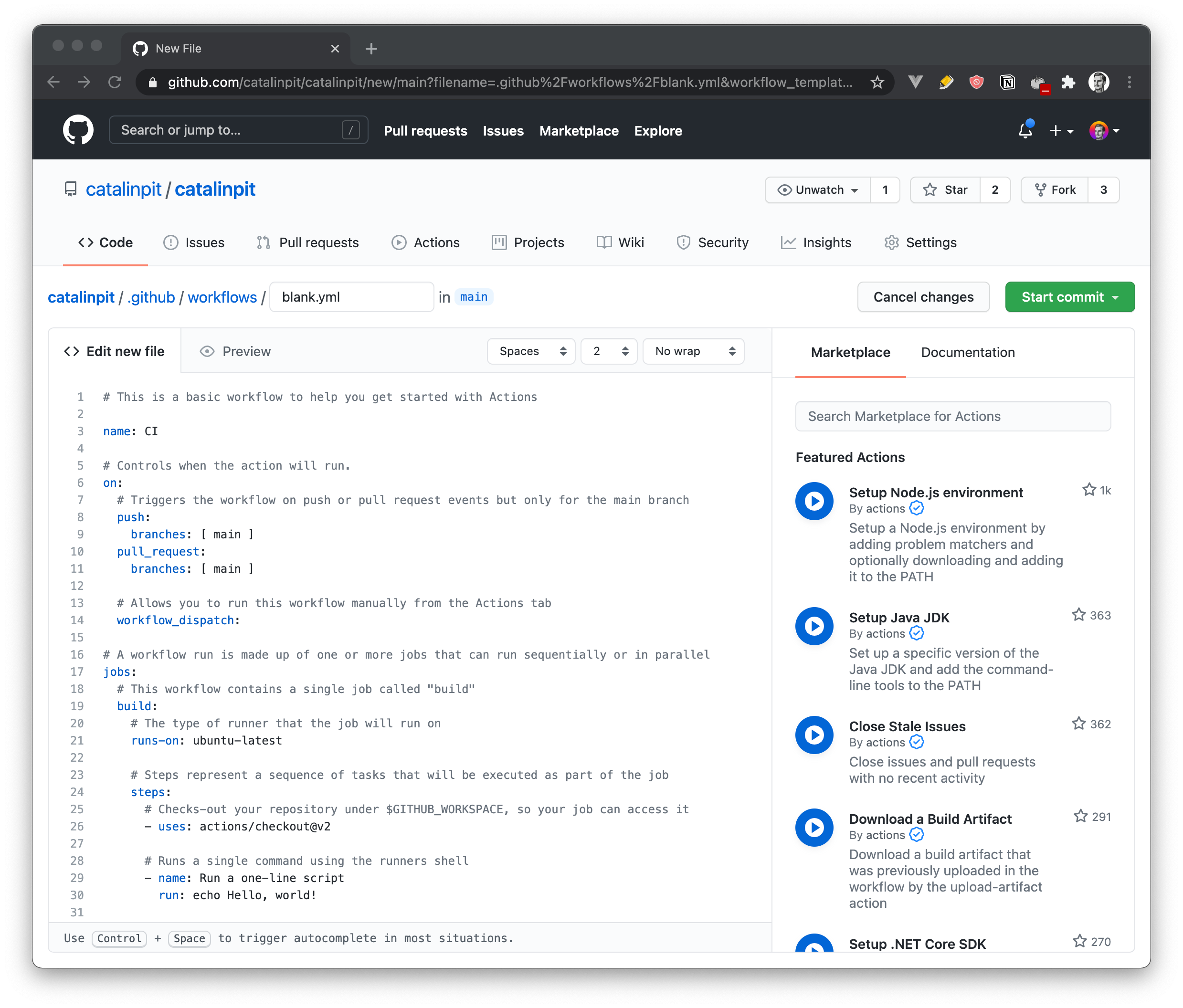
The above image shows what you see when you set up a new workflow. It comes with a bunch of code you do not need.
First of all, change the file name at the top (where it says blank). After that, delete all the code from the file.
You can find the workflows you need here:
Note: You do not need to create the folders .github/workflows/ in your repository. They are created automatically when you set up the GitHub actions. However, because I set up everything before the tutorial, I already have them in place. As a result, you can use them to copy the code needed for your GitHub actions.
Fetch YouTube videos
For this tutorial, I will show you how to create a workflow to fetch your latest YouTube videos. However, the process for fetching the latest blog articles is similar.
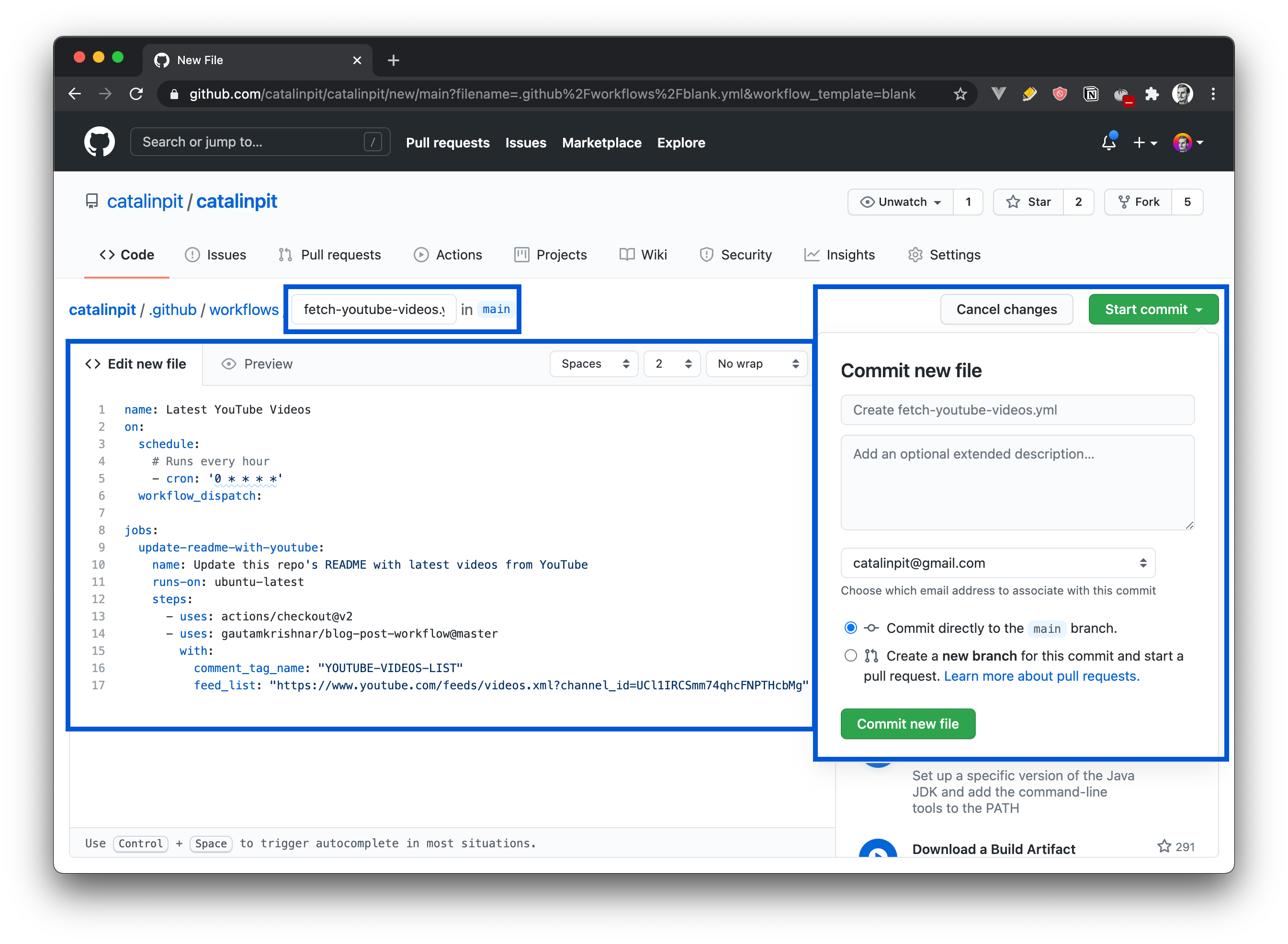
The image above shows how to create the YouTube fetching workflow. The blue rectangles show what I modified and where you have to click to start the workflow. The steps are as follows:
- Name the workflow
- Add the code - get it from here
- Click on
Start commitand then onCommit new file
After you commit the new file, the workflow runs automatically. Additionally, it will run daily to fetch your new videos.
To fetch the blog articles, follow the same process but use this code.
8. Set up the template
The last step you have to do to display the latest articles/videos is to go to the README and add the following code snippet:
---
📺 Latest YouTube Videos
<!-- YOUTUBE-VIDEOS-LIST:START -->
<!-- YOUTUBE-VIDEOS-LIST:END -->
▶ [...more YouTube videos](https://www.youtube.com/channel/UCl1IRCSmm74qhcFNPTHcbMg?sub_confirmation=1)
---
📘 Latest Blog Articles
<!-- BLOG-POST-LIST:START -->
<!-- BLOG-POST-LIST:END -->
▶ [...more blog articles](https://catalins.tech)
---
The above snippet is a simple markdown code with one exception. You can see the tags youtube-videos-list and blog-post-list, which are used in the GitHub actions. They tell the actions where the new videos/articles should be added. If you remove them, your README will not be updated anymore. Other than that, the code is self-explanatory.
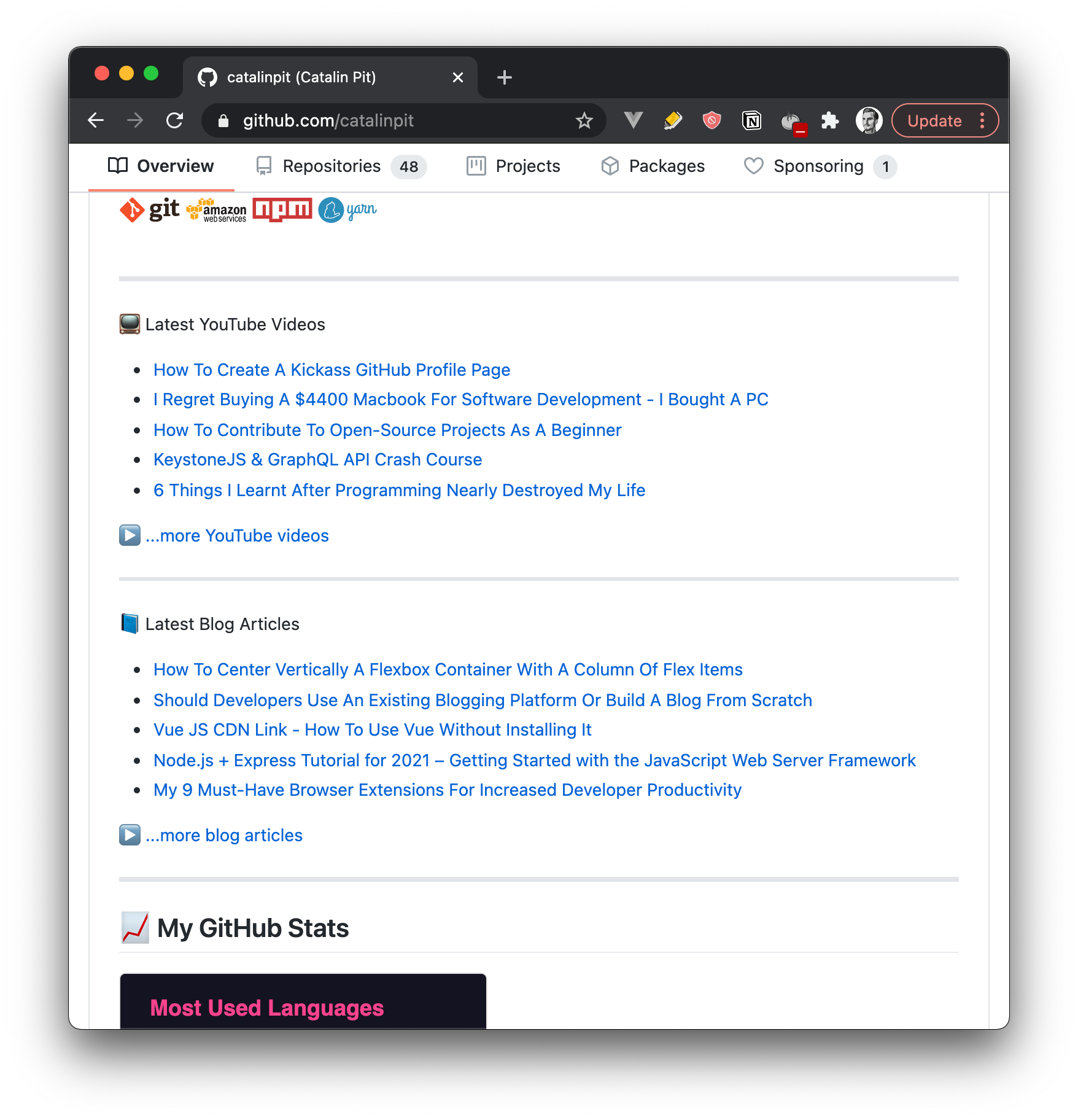
The image above illustrates how the profile page looks after setting up the GitHub actions. It displays your latest blog articles and/or YouTube videos automatically.
9. GitHub stats
The next and last step is to add GitHub statistics to your profile. You can see below how they look like on my profile.
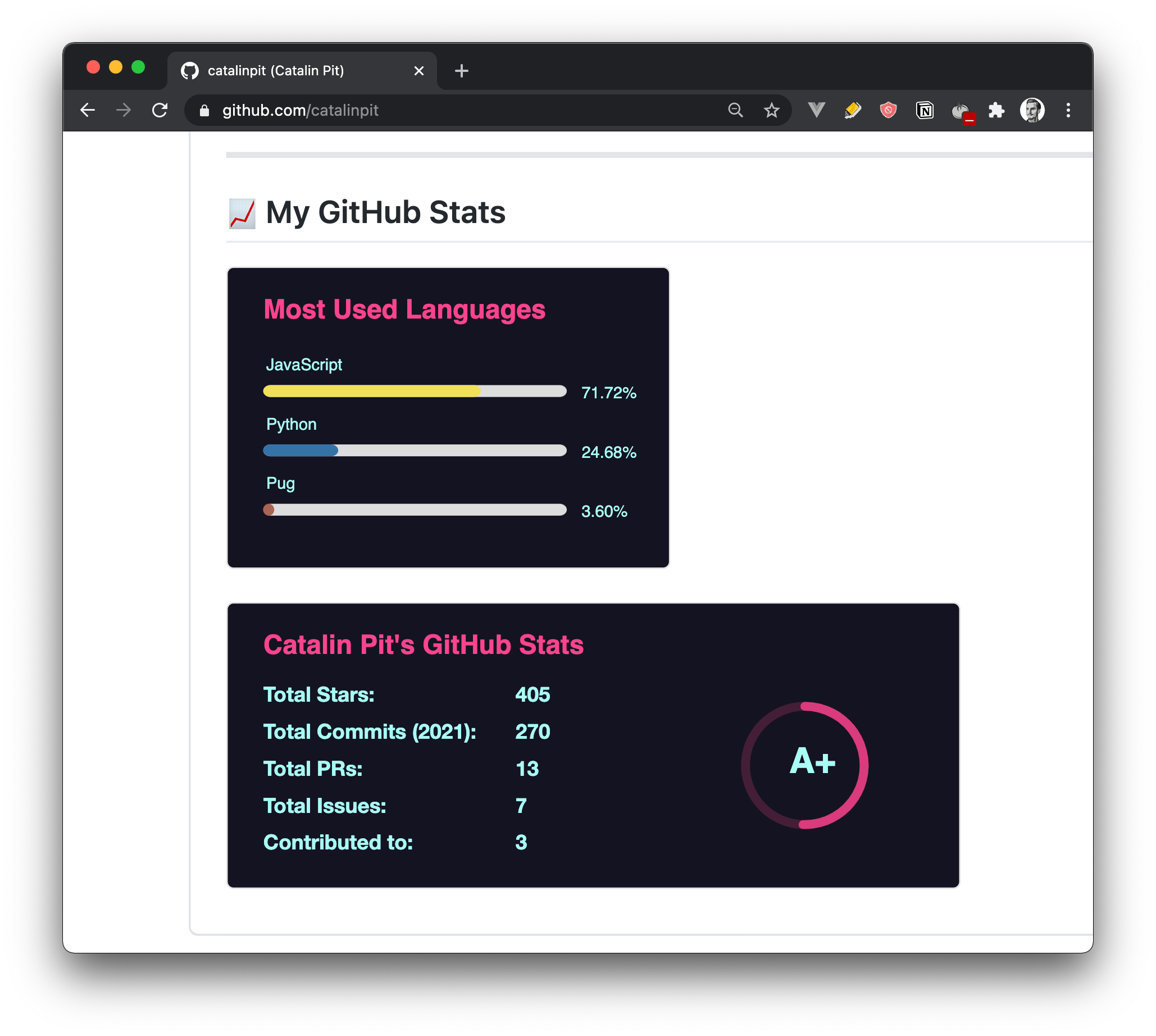
Add the following snippet to your README.md, but make sure that you change <your_GitHub_username> to your GitHub username.
---
## 📈 My GitHub Stats
[](https://github.com/anuraghazra/github-readme-stats)
[](https://github.com/anuraghazra/github-readme-stats)
If you look closely at the links, you can see that they have query parameters. They allow you to customize the stats.
For instance, in the above link, you can see hide=java,html,css, which hides those programming languages from the stats. Also, you can see theme=radical, which changes the theme of the images. You can use the following themes:
- dark
- radical
- merko
- gruvbox
- tokyonight
- onedark
- cobalt
- synthwave
- highcontrast
- dracula
Besides hiding programming languages and using custom themes, you can also toggle options on/off, and you can customize other things such as the line height, custom title, and so on. However, for more GitHub stats or customizations, I recommend you to check the official repository.
Conclusion
Well done for creating an awesome GitHub profile! If you want to see other great GitHub profiles and inspire, you can check the website Awesome Github Profile.

