In this article, you will see how to pass command-line arguments to your Node.js application. You will also learn how to access them.
However, before proceeding further, let's start with some basic stuff. To run a Node.js application, you run the following command in your terminal:
node index.js
Thus, when you run the above command, you can pass any number of arguments. When it comes to command-line arguments, there are two types:
- single arguments such as
node index.js myArg - key-value arguments such as
node index.js myArg=myVal
Now, the next step is to learn how you can access these arguments in your Node.js application.
The process object
In Node.js, the process object is a global object and contains information about the current Node processes. Since it's a global object, you have access to it directly even though you do not import it into your application.
Moreover, the process object has a property called argv, which is an array that contains the command-line arguments.
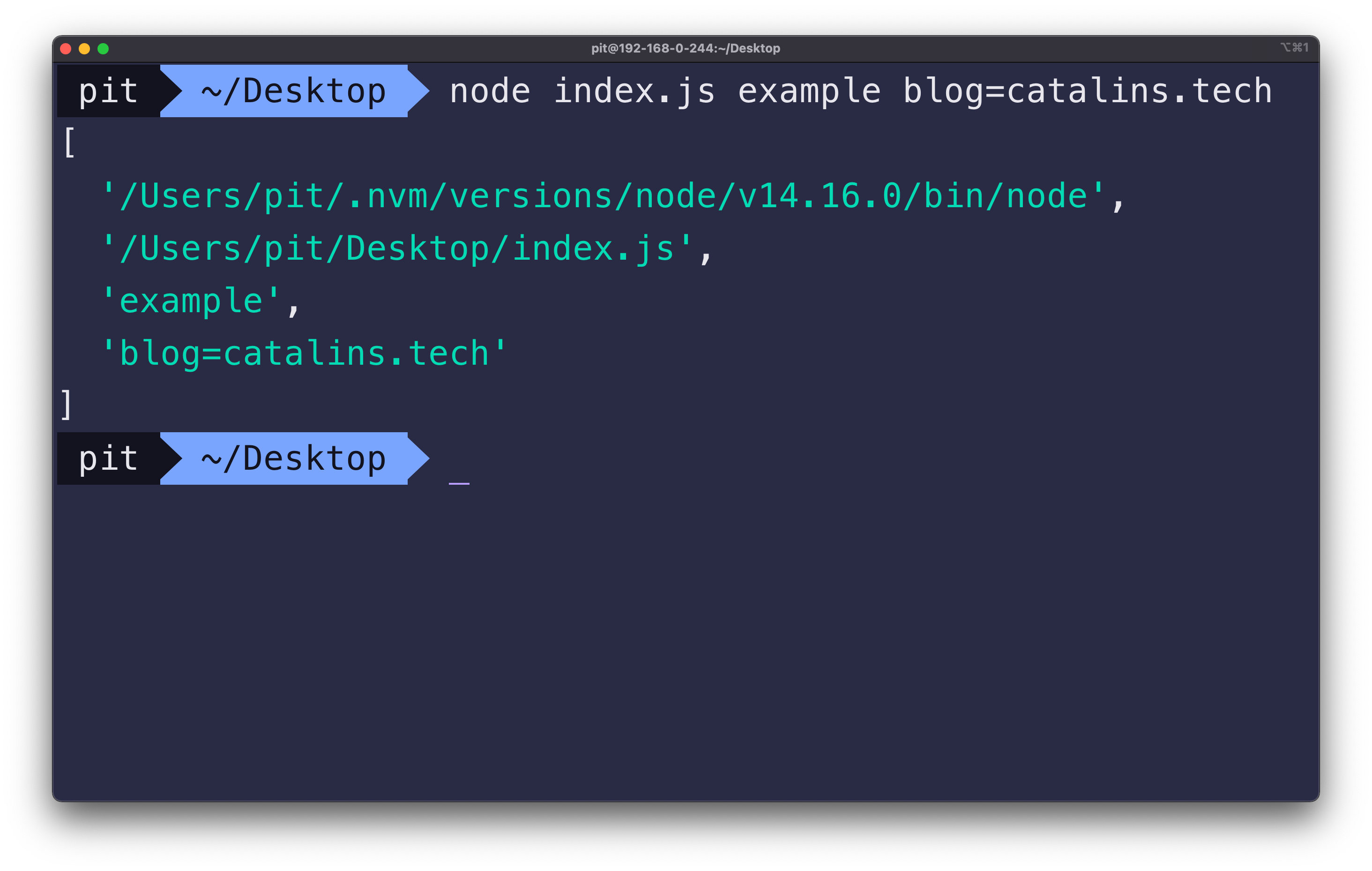
Figure 1
Figure 1 illustrates the array of arguments. However, you can see that there are other items in the array. Let's see what they are:
- The first element represents the path of the "node" command.
- The second element is the path of the file being executed - in this case, it is
index.js. - The third and fourth elements are the command-line arguments.
Note: The array can have more elements. It depends on how many arguments you pass to the application.
Access arguments in Node.js
The first two elements in the arguments array will always be the path of the "node" command and the path of the file being executed. Thus, you can get rid of them by using the JavaScript splice method.
const arguments = process.argv.splice(2);
The above line removes the first two entries and keeps the rest. It then stores the remaining array in the constant arguments.
Now you can loop over the arguments or access them individually as follows:
const myArgs = arguments.map(argument => {
console.log(argument);
});
console.log(arguments[0]);
console.log(arguments[1]);
If you run the above code, your Node.js application will output your arguments to the terminal. Thus, this is how you can use command-line arguments in your Node.js application.
For more information about the
processobject, I recommend reading the Node.js official documentation.